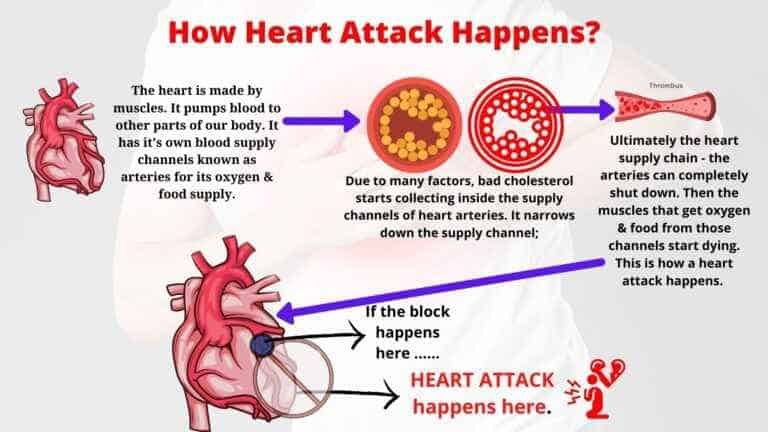
How does heart attack or myocardial infarction occur?
Heart attack commonest (around 95%) cause is atherosclerosis, due to which blockage happens inside the arteries of the heart. If the artery gets blocked, then the heart muscle that it supplies are starved of oxygen & it starts dying. This causes extreme chest pain. That is why the commonest symptom of heart attack is chest pain.
What is atherosclerosis? Atherosclerosis is a composite of cholesterol waste product that is trapped inside arteries. Their size is increased over a period of time due to various risk factors like obesity, diabetes, un-natural choice of foods, stress, smoking, etc.
The increased size of atherosclerotic plaque can hamper blood flow to the heart muscle & can cause pain upon exertion. But taking rest most of these get relieved. These are known as Angina episodes.
When the artery gets completely occluded then the heart muscle start that gets a supply of oxygen from the artery starts dying. That causes excruciating pain and thus heart attack or myocardial infarction.
Causes of Heart Attack
Arteriosclerosis
What normally causes a heart attack is an atherosclerotic plaque rupture on an artery supplying the heart muscle. Plaques can turn out to be unstable, which causes rupture, resulting in the formation of a blood clot that obstructs the artery-it may happen within minutes. Obstruction of an artery may result in tissue death in the tissue being supplied by that artery. Atherosclerotic plaques may exist for years before they can cause symptoms.
The continuous formation of fibrous tissue and cholesterol in plaques in the coronary arteries wall for years is described as atherosclerosis. The condition is defined by continuous inflammation of the walls of the arteries. Inflammatory cells, specifically macrophages, move into damaged arterial walls. As time goes by, they become filled with cholesterol products, specifically LDL, and changes to foam cells. A cholesterol core forms as foam cells die.
As a response to growth factors produced by macrophages, smooth muscle and other cells move into the plaque and act, bringing about stabilization. A stable plaque may appear as a thick fibrous cap with calcification. When inflammation occurs, the cap may ulcerate or become thin. Blood flow associated pressure may cause plaques, mostly the thin-lined ones, to rupture and induce a blood clot formation. The cholesterol crystals have been identified to cause plaque rupture through inflammation and mechanical injury.
Reference of Atherosclerosis.
Other causes
Besides atherosclerotic disease, a heart attack may result from other causes.
- As heart rate increases the It may be due to inadequate blood supply caused by high oxygen demands in cases of –
- low blood pressure,
- reduced number of red blood cells in the bloodstream,
- hyperthyroidism,
- rapid heart rate,
- and fever.
- Damages from procedures like coronary artery bypass grafts or percutaneous coronary intervention may lead to a heart attack.
- Coronary arteries spasm may result in blockage.
If disrupted blood flow to the heart persists, it induces a process referred to as ischemic cascade; the heart cells around the blocked coronary artery die, usually through necrosis, and do not grow back. A collagen scar replaces the dead cells.
What causes the pain in a heart attack?
When an artery is blocked, ATP production in mitochondria is affected due to inadequate oxygen in the cells. ATP is vital for sustained electrolyte balance. This results in an ischemic cascade of intracellular changes necrosis, and apoptosis of impaired cells. Cells within the region with the worst blood supply, i.e., endocardium, are more prone to damage. First, ischemia affects this area, and then tissue death occurs within 15-30 minutes of limited blood supply.
The severity and position of a heart attack or myocardial infarction depend on –
- the affected artery,
- the blockage’s integrity,
- length of the blockage,
- oxygen demand,
- presence of collateral blood vessels,
- position, size of the block,
- and success of interventional procedures.
Myocardial scarring and tissue death interfere with the heart’s pathways, normal functioning, and weaken the affected regions. The location and size increase the risks of inflammation, abnormal heart rhythms, and the heart wall’s rupture that may have injurious outcomes.
Can a heart attack happen without blockage?
Yes, of course. Heart is made by muscle. It pumps blood throughout your body. It beat 60 to 100 bpm in normal parents at rest or with mild works. Heart attack means, if the heart muscle is damaged by any means and doctor can find the damage by means of doing blood tests, ECH, Echocardiography etc. That means you you are having heart attack.
Here are few reasons where your you have heart attack without any blockage –
- Hypercoagulable state – This means your blood has become so thick that it is blocking the blood supply to the heart. Here are few instances – after surgery, cancer, birth control pills, anti-phospholipid syndrome, etc.
- Vasculitis – Inflammation in the arteries that are supplying blood to the heart i.e Takayasu vasculitis.
- Viral myocarditis – Inflammation of the heart muscle leads to heart damage in viral infection due to highly active inflammatory chemicals of the body that attack the virus, also attack the heart muscle. And the heart muscle gets damaged.
- Stress Cardiomyopathy – Due to sudden & intense stress, the heart muscles get dysfunctional and damaged. Also known as “broken heart syndrome”. It proves that stress can damage your heart.
- Peripartum cardiomyopathy – Here due to some unknown reason the heart muscle gets dysfunctional in the last three months of pregnancy and/or first six months after pregnancy.
- Angiogram/angioplasty and CABG – During these surgeries, the heart muscles can get damaged.
So, Heart attack can happen without the blockage in the heart (coronary) arteries.





